PAH Residues in Soil from a Superfund Site
EPA Superfund sites were funded to reclaim dangerously toxic land by cleaning the soil and water of contaminants such as PAHs left behind by creosote wood treatment plants, industrial sludge lagoons, and oil and tar sources. The utility of the PDD is illustrated in this analysis of PAH residues in a soil sample from an actual Superfund site. The chromatogram also illustrates the ability of the PDD to handle complex matrices.
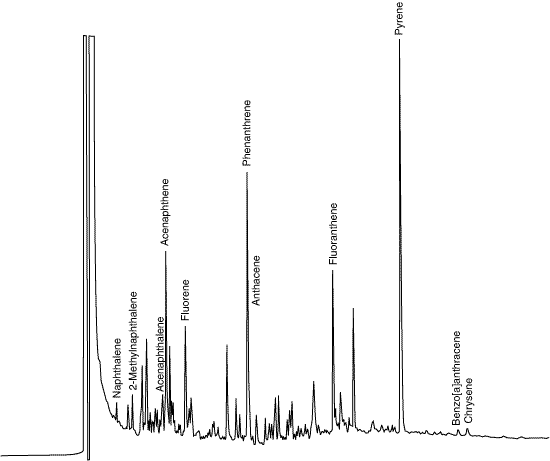
Courtesy of Ohio University, Dept. of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Hongyan Zhang and Anthony R. J. Andrews, Ph.D.
| Run conditions | |
|---|---|
| Sample | EPA Superfund soil (1 g) |
| Sample volume | 2 µl (solvent microextraction), 25:1 split |
| Injector temp | 275°C |
| Detector mode | Helium photoionization |
| Discharge gas | Helium |
| Dopant gas | None |
| Detector temp | 300°C |
| Column | RTX-35, 30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 µm |
| Column temp | 200°C for 1 min, to 250°C at 45°C/min (1 min), to 300°C at 45°C/min (11 min) |
| Attenuation | 1 |

